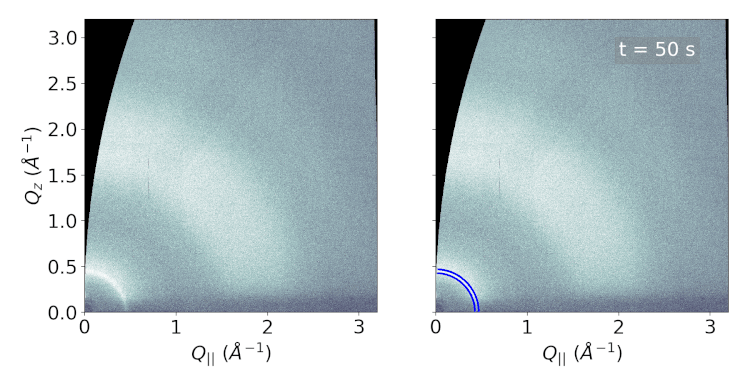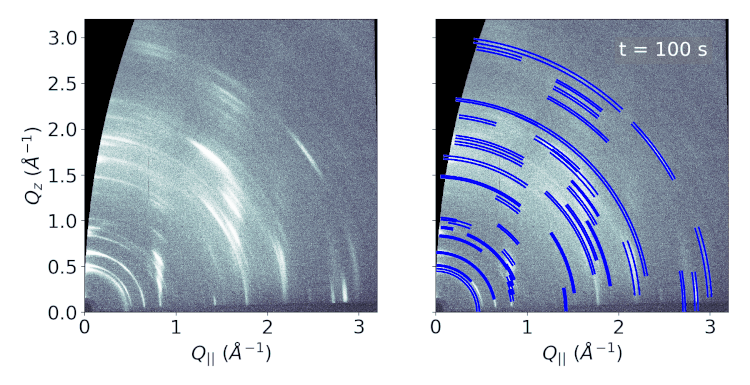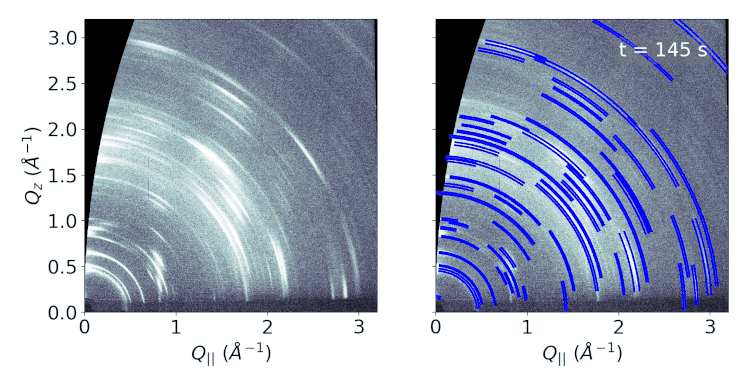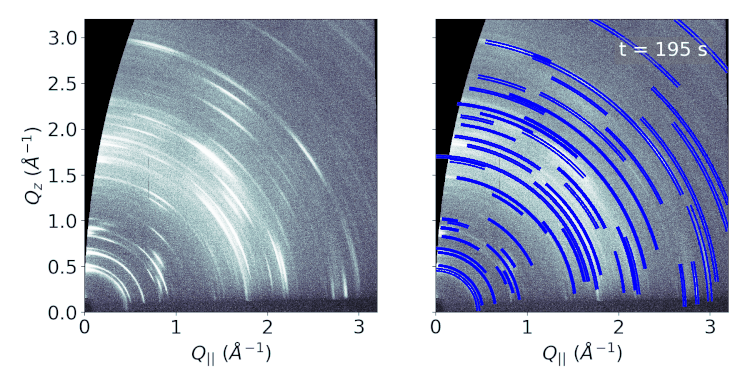
 The physically relevant information contained in the GIWAXS data is the
positions and widths of the scattering features. Having access to this information enables
the possibility of detailed analysis such as crystal structure determination or the temporal
evolution of individual crystal phases. The combination of varying scattering backgrounds,
high noise and experimental artifacts makes it challenging to automate the extraction of
GIWAXS scattering features with any classical algorithms. Machine learning approaches have
been shown to vastly outperform classical approaches in that regard, being able to separate
objects from highly noisy and complex backgrounds, with applications ranging from medicine
to astrophysics. There are a multitude of modern object detection or segmentation models for
data in image form. Such models use a backbone consisting of a deep convolutional neural
network to extract feature maps from images, followed by a head which performs additional
regression or classification tasks resulting in the final output. We treat the GIWAXS peak
extraction as an object detection task and modify the Faster R-CNN object detection model
for our specific problem [1]. We want our approach to perform well on any input GIWAXS
image, thus we train the model using simulated GIWAXS images with peak positions and sizes
randomly generated. In order to make the model as robust as possible we include different
types of noise, backrounds and experimental artifacts in the simulations. The trained
object detection model is able to extract peak coordinates in a fraction of a second.
The physically relevant information contained in the GIWAXS data is the
positions and widths of the scattering features. Having access to this information enables
the possibility of detailed analysis such as crystal structure determination or the temporal
evolution of individual crystal phases. The combination of varying scattering backgrounds,
high noise and experimental artifacts makes it challenging to automate the extraction of
GIWAXS scattering features with any classical algorithms. Machine learning approaches have
been shown to vastly outperform classical approaches in that regard, being able to separate
objects from highly noisy and complex backgrounds, with applications ranging from medicine
to astrophysics. There are a multitude of modern object detection or segmentation models for
data in image form. Such models use a backbone consisting of a deep convolutional neural
network to extract feature maps from images, followed by a head which performs additional
regression or classification tasks resulting in the final output. We treat the GIWAXS peak
extraction as an object detection task and modify the Faster R-CNN object detection model
for our specific problem [1]. We want our approach to perform well on any input GIWAXS
image, thus we train the model using simulated GIWAXS images with peak positions and sizes
randomly generated. In order to make the model as robust as possible we include different
types of noise, backrounds and experimental artifacts in the simulations. The trained
object detection model is able to extract peak coordinates in a fraction of a second.